Welcome to the polishing phase of AI image creation! While AI tools are incredibly powerful, they are rarely perfect on the first try. You will often encounter specific "hallucinations" or errors that require a human touch to fix. Common problems include:
- Incorrect Visual Style: The image doesn't match the intended mood or aesthetic.
- Presence of Extra Detail: AI adds "hallucinated" objects, extra limbs, or unnecessary clutter.
- Absence of Important Detail: The AI ignores a core part of your prompt.
- Mistakes in Small Details: Glitches in textures, eyes, or hands.
- Garbled Text and Signs: Modern AI can render legible words but struggles to use it properly within the image.
Imagine you want to create an educational poster. You ask the AI for: "An alphabet where every letter is associated with an animal."
We ran this prompt with an old gpt4-o model. Look at these funny mistakes it made. While all the words are spelled correctly, the word-letter-animal association is poor. Could you find all the mistakes?

Of course, newer versions of the model will make less mistakes. However, they will still do them from time to time, so be careful.
Prompt Recommendations for Text Issues:
- Isolate the Task: Instead of asking for a whole alphabet, generate one letter at a time and then combine them in another tool.
- Use Post-Processing: Often, it is faster to generate the image without text and add the correct text later using a design tool like Canva or Photoshop.
While AI gets better and better with text on images, especially the English text, it still can struggle with other types of signs, symbols and notation. Here are more examples:
Math formulas
You don't need to know math to spot errors and problem on this generated math textbook:

Road sign
This road sign is clearly not a correct US road sign.

Musical score generation
Even if you don't know any of the music theory, you can clearly see that something is wrong with some symbols on this image of a musical score. And if you do, you can notice that the melody, grouping and the whole score in general does not make sense.

To sum up: AI is a powerful tool, but has limitations. Be aware of them when using it.
Another common issue occurs when the AI takes your words too literally. If you ask for a "wide-angle shot of a moonscape," the AI might generate the surface of the moon but then place another moon in the sky.
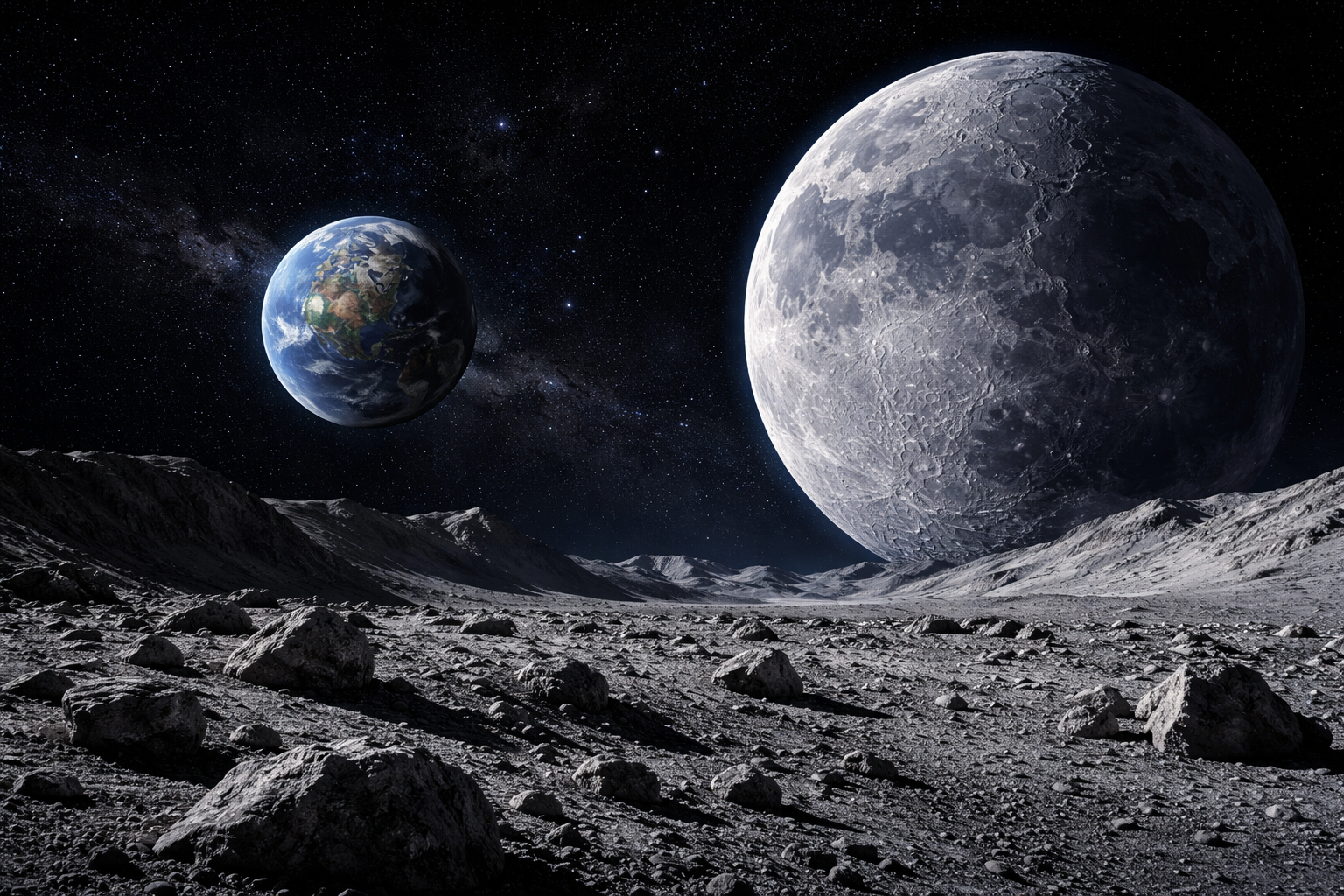

This happens because the AI uses semantic mapping: if the word "moon" appears in the prompt, the AI's "brain" identifies the object "moon" and feels compelled to include it as a visible object, even if it doesn't make logical sense in a landscape on the moon.
Prompt Recommendations for Mapping Issues:
- Use Synonyms: Instead of "moonscape," try "lunar surface" or "view from a crater floor looking at the stars."
- Use Negative Prompts: If your tool supports it, add
moonto the negative prompt while keepinglunar surfacein the main prompt. - Direct the Camera: Specify the perspective, such as "POV from the ground looking toward the horizon," to ground the AI's "camera" and prevent it from adding floating objects.
AI can struggle with basic logic, counting, and structural organization. This is because AI doesn't "calculate" or "reason" through a layout; it predicts what a layout looks like based on patterns.
1. The Counting Problem AI models are notoriously bad at counting. If you ask for something as simple as "9 circles connected with a single line," the AI might generate 7, 8, or 10. It understands the "vibe" of circles and lines, but it doesn't actually count the objects as it renders them.
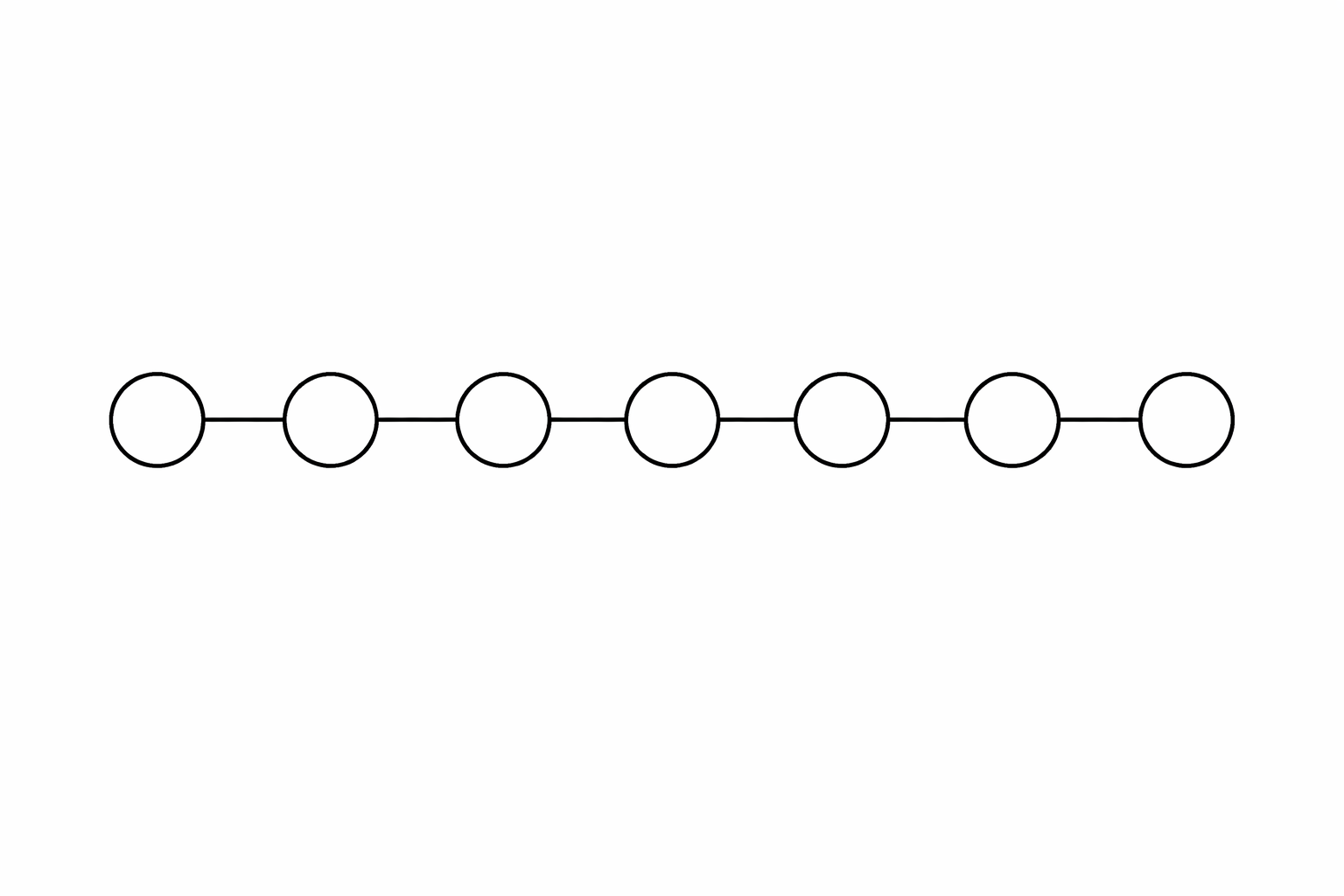
2. Messy Diagrams and Graphs Logic-based structures like maps or flowcharts often fall apart. For example, if you ask for a "Generate an image showing a schematic map of a roguelike video game, where each room connects EXACTLY with two following rooms featuring different prizes" the AI might produce an image that does look like a map, but the connections will be incorrect, not following the strict requirement of each rooms connecting to two other rooms.
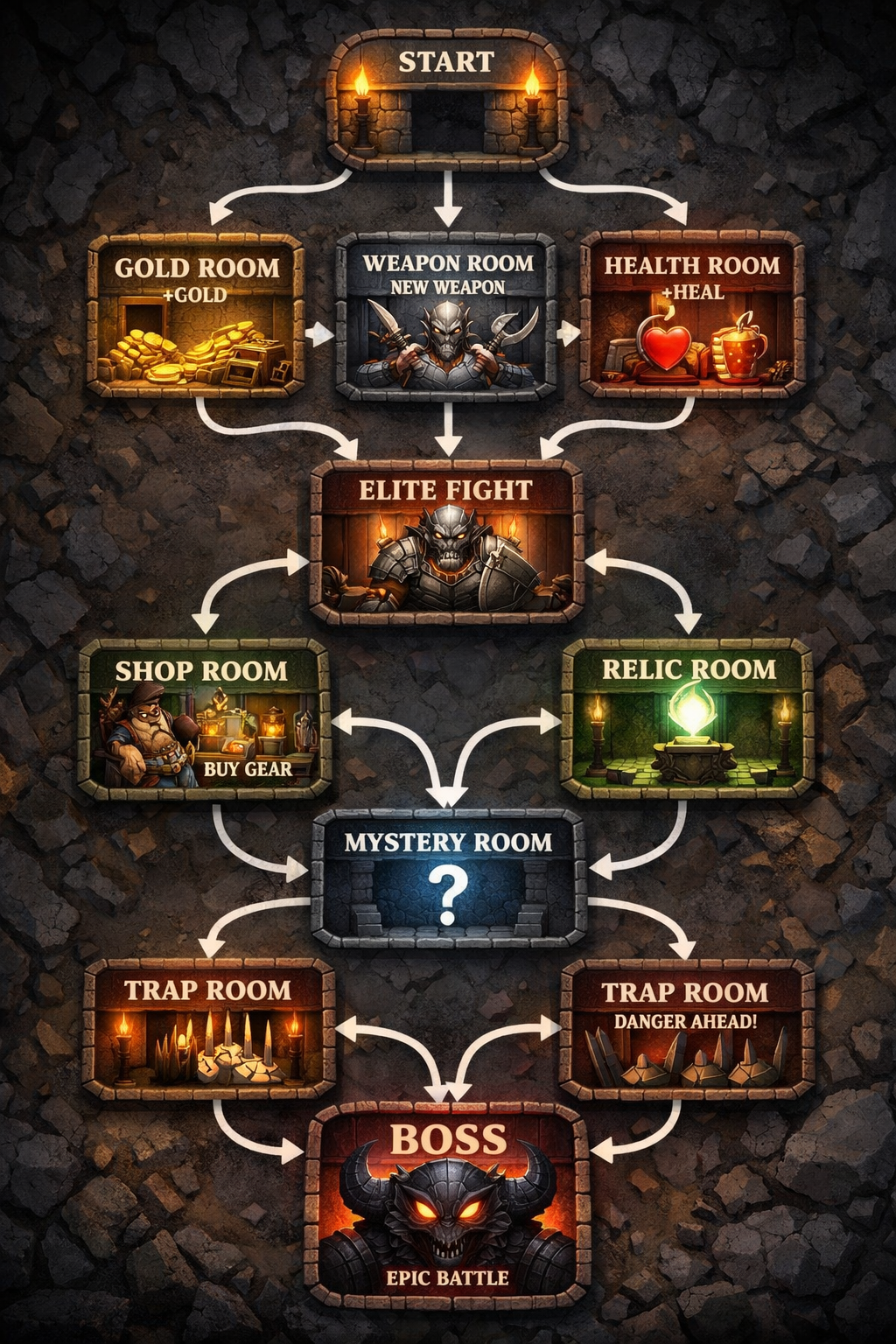
Prompt Recommendations for Structural Issues:
- Generate Components, Not Systems: Instead of asking for a full diagram, ask for the individual elements (like the city icons) and assemble the graph yourself in a design tool.
It is important to remember that the technical mistakes discussed above—like extra moons or messy text—are often the easiest to fix. Usually, a few "re-rolls" (generating the image again) or a quick fix in Photoshop will solve them.
The real challenge of AI generation is not fixing glitches, but getting the image to look exactly as you envisioned it. Achieving the proper style, the right emotional tone, and the perfect level of detail requires a deeper understanding of prompt parameters.
For instance, you might say:
Create a corporate logo with a minimal color palette, a clean, modern style, and balanced symmetry.
Here, clarity of description directs the AI to keep the design simple and focused, level of detail ensures the minimal color palette is clearly defined, style reference emphasizes a modern look, and composition notes call for balanced symmetry.
Modern AI tools allow you to work with the image generation iteratively, fixing images or adding details to the images that already exist in your dialogue with the model.
Once you're comfortable refining single images, try merging multiple AI outputs. This step is especially useful if you want a richer, more layered scene — such as combining a product photo with a branded background — or ensuring a consistent style across different elements.
-
Layering
– Prompt 1:
Generate a pirate ship in a stormy sea, oil painting style.
– Prompt 2:Generate a giant kraken rising from a stormy sea, in the same style.
– Merge Request:Combine the pirate ship and kraken into one scene, keeping the stormy atmosphere and consistent oil painting style.
– Why It Works: Layering adds excitement and depth while maintaining a cohesive aesthetic. This can also unify multiple brand elements to tell a richer story.

-
Masking
– Prompt:
Give the spaceship a metallic surface, preserving its current color scheme.
– Rationale: This focuses on adjusting only the spaceship's surface appearance without changing its original palette. It helps you preserve what you love about your image while making targeted improvements. -
Style Transfer
– Prompt:
Apply the painterly feel from my existing forest image to a new dragon illustration, so both match visually.
– Rationale: This references a previously defined aesthetic, allowing you to seamlessly unite different images under one cohesive style. This is perfect for multi-piece campaigns where every visual needs a consistent look.
Whether you're perfecting a brand logo, crafting fantasy environments, or simply refining a personal project, these prompts and techniques give you the flexibility to guide AI with confidence. Every small tweak brings you closer to creating images that look and feel exactly the way you want.
