Welcome to the final lesson of our "Developing a Personal Tutor Web Application With Django" course! In the previous lesson, you enhanced your personal tutor application by adding query suggestions, making it more user-friendly and efficient for students. Today, we will complete our application by focusing on styling the interface to make it visually appealing and professional. Styling is crucial in educational web applications, as it enhances the learning experience by providing a clean and intuitive interface. We will use CSS to achieve this, ensuring that our tutor application not only functions well but also looks great.
To style our personal tutor interface, we first need to create a directory for our static files, such as CSS. Django provides a built-in static files system that makes it easy to manage and serve these files.
-
Create the Static Directory: Inside your Django app directory (for example,
project/tutor/), create a folder namedstatic. This is where you'll store yourCSSfile. -
Configure Static Files in Django: Make sure your Django settings include the following configuration for static files (these are usually set by default):
Django's static files system allows you to organize and serve CSS, JavaScript, and image files efficiently. By placing your CSS file in the static directory, you ensure that it can be easily referenced in your templates.
With the static directory set up, the next step is to create a CSS file and link it to your HTML template using Django's template tags.
-
Create the CSS File: In your app's
staticdirectory, create a file namedstyle.css. This file will contain all the styles for your application. -
Link the CSS File in HTML: Open your
tutor.htmltemplate and add the following lines at the top of the file to load static files and link yourCSS:
The {% load static %} tag enables the use of static file references in your template. The <link> tag uses {% static 'style.css' %} to generate the correct URL for your CSS file, ensuring that the styles are applied to your HTML elements.
Below, we’ll break down the CSS of your style.css file into logical sections, explaining the purpose and effect of each part.
Start by ensuring the page takes up the full viewport height and uses a modern font. The body is set as a flex container with a column layout, which helps in structuring the main sections vertically.
The header is styled to be visually distinct, centered, and padded, with a subtle background color to separate it from the rest of the content.
The suggestions section uses flexbox to center the suggestion buttons and add spacing between them. The buttons themselves are styled to be vibrant and inviting.
The chat container is set up as a flex column, centered on the page, and responsive. It uses a maximum width for readability and hides overflow to keep the layout clean.
The messages area is given a border, padding, and scrollable overflow to handle long conversations. Each message is spaced and padded for readability.
The input section uses flexbox for layout, with spacing between elements. The input field is styled to fill available space, and buttons are styled for consistency and usability.
When no CSS is applied, the interface appears plain and unstructured. All elements — headers, buttons, chat messages, and input fields — use default browser styles. This results in a basic layout with minimal spacing, inconsistent fonts, and no visual hierarchy. Buttons and input fields look generic, and the overall experience feels less engaging and less professional. Let's visualize an example:

After applying the provided CSS, the interface transforms into a visually appealing and user-friendly environment. The header is centered and stands out, suggestion buttons are vibrant and inviting, and the chat container is neatly organized with clear separation between user and assistant messages. The input section is well-aligned and easy to use, and the entire application adopts a consistent font and color scheme. These enhancements not only make the application look modern and professional but also improve usability and the overall learning experience. Here's how it looks now:
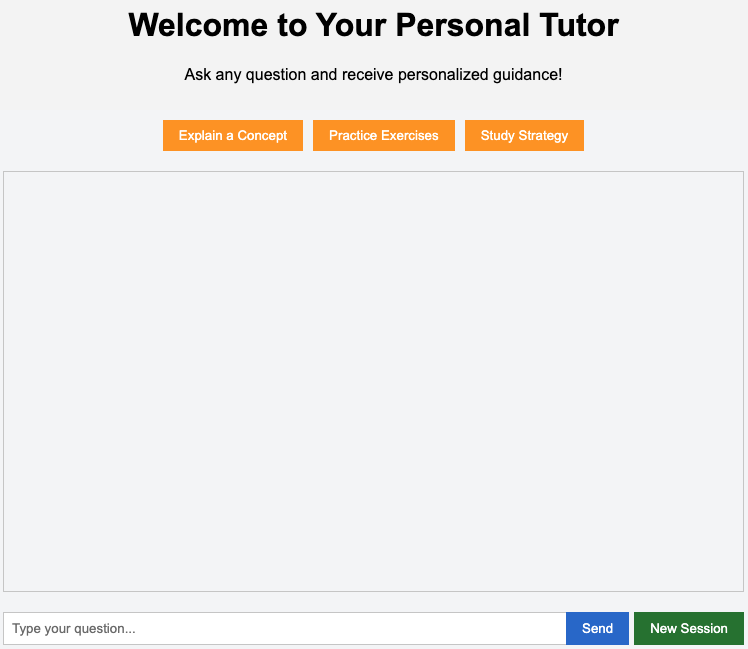
In this lesson, you learned how to style your personal tutor interface using CSS. We set up a static directory in Django to serve static files and linked a CSS file to your HTML template. We then applied a comprehensive set of styles to the header, suggestions, chat container, messages, and input section, creating a visually appealing and user-friendly educational interface.
As you move on to the practice exercises, focus on experimenting with different styles to achieve your desired look and feel. This hands-on practice will deepen your understanding and help you create a professional-looking interface that enhances the tutoring experience for students.
